OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA)
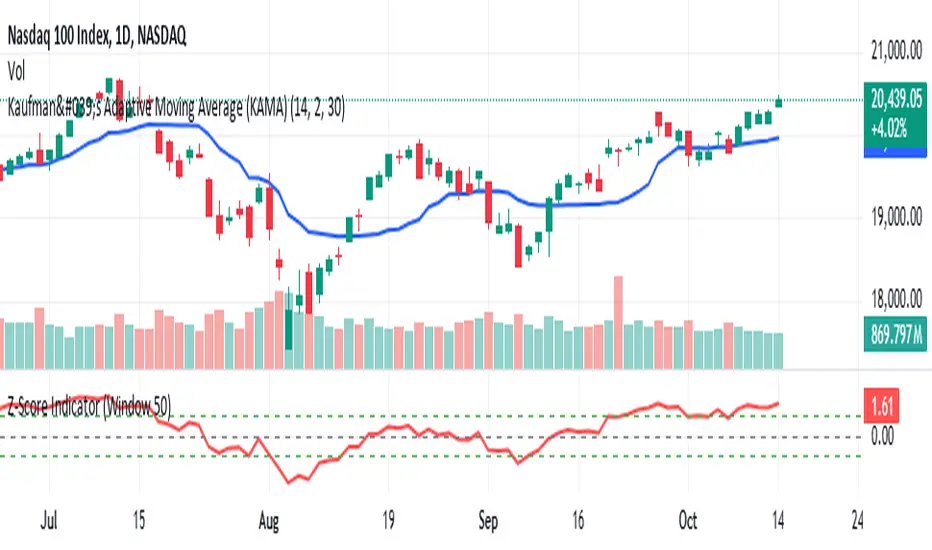
Another simple easy to use indicator that incorporates mean reversion and trend following.
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) is an indicator developed by Perry Kaufman that adjusts its sensitivity based on market volatility. It is designed to react more quickly during trending markets and slow down in sideways or volatile markets. The primary idea is that in a trending market, the moving average should be more sensitive to price changes, while in a non-trending market, it should be less responsive to noise.
KAMA Formula
The formula for the Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average is:
Efficiency Ratio (ER): Measures the efficiency of price movement over a given period.
ER
=
Smoothing Factor
Volatility
=
Sum of absolute price change
Sum of absolute price movement
ER=
Volatility
Smoothing Factor
=
Sum of absolute price movement
Sum of absolute price change
The Efficiency Ratio is calculated by taking the price change over a defined period and dividing it by the total price movement (which is the sum of absolute price changes).
Smoothing Constant (SC): This is a factor used to adjust the moving average's responsiveness:
SC
=
ER
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
+
(
1
−
ER
)
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
SC=ER×(2/(n+1))+(1−ER)×(2/(n+1))
where n is the length of the moving average period.
Steps to Calculate KAMA:
Efficiency Ratio (ER):
Calculate the sum of absolute price changes over the chosen period.
Calculate the sum of absolute price movements over the same period.
Smoothing Constant (SC):
Use the Efficiency Ratio to adjust the smoothing factor.
KAMA Calculation:
The initial KAMA is the simple moving average (SMA) of the first n periods.
For subsequent periods, KAMA is calculated using a formula based on the smoothing constant and previous KAMA values.
experiment with the variables as you like!!
Kaufman's Adaptive Moving Average (KAMA) is an indicator developed by Perry Kaufman that adjusts its sensitivity based on market volatility. It is designed to react more quickly during trending markets and slow down in sideways or volatile markets. The primary idea is that in a trending market, the moving average should be more sensitive to price changes, while in a non-trending market, it should be less responsive to noise.
KAMA Formula
The formula for the Kaufman Adaptive Moving Average is:
Efficiency Ratio (ER): Measures the efficiency of price movement over a given period.
ER
=
Smoothing Factor
Volatility
=
Sum of absolute price change
Sum of absolute price movement
ER=
Volatility
Smoothing Factor
=
Sum of absolute price movement
Sum of absolute price change
The Efficiency Ratio is calculated by taking the price change over a defined period and dividing it by the total price movement (which is the sum of absolute price changes).
Smoothing Constant (SC): This is a factor used to adjust the moving average's responsiveness:
SC
=
ER
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
+
(
1
−
ER
)
×
(
2
/
(
𝑛
+
1
)
)
SC=ER×(2/(n+1))+(1−ER)×(2/(n+1))
where n is the length of the moving average period.
Steps to Calculate KAMA:
Efficiency Ratio (ER):
Calculate the sum of absolute price changes over the chosen period.
Calculate the sum of absolute price movements over the same period.
Smoothing Constant (SC):
Use the Efficiency Ratio to adjust the smoothing factor.
KAMA Calculation:
The initial KAMA is the simple moving average (SMA) of the first n periods.
For subsequent periods, KAMA is calculated using a formula based on the smoothing constant and previous KAMA values.
experiment with the variables as you like!!
오픈 소스 스크립트
트레이딩뷰의 진정한 정신에 따라, 이 스크립트의 작성자는 이를 오픈소스로 공개하여 트레이더들이 기능을 검토하고 검증할 수 있도록 했습니다. 작성자에게 찬사를 보냅니다! 이 코드는 무료로 사용할 수 있지만, 코드를 재게시하는 경우 하우스 룰이 적용된다는 점을 기억하세요.
면책사항
해당 정보와 게시물은 금융, 투자, 트레이딩 또는 기타 유형의 조언이나 권장 사항으로 간주되지 않으며, 트레이딩뷰에서 제공하거나 보증하는 것이 아닙니다. 자세한 내용은 이용 약관을 참조하세요.
오픈 소스 스크립트
트레이딩뷰의 진정한 정신에 따라, 이 스크립트의 작성자는 이를 오픈소스로 공개하여 트레이더들이 기능을 검토하고 검증할 수 있도록 했습니다. 작성자에게 찬사를 보냅니다! 이 코드는 무료로 사용할 수 있지만, 코드를 재게시하는 경우 하우스 룰이 적용된다는 점을 기억하세요.
면책사항
해당 정보와 게시물은 금융, 투자, 트레이딩 또는 기타 유형의 조언이나 권장 사항으로 간주되지 않으며, 트레이딩뷰에서 제공하거나 보증하는 것이 아닙니다. 자세한 내용은 이용 약관을 참조하세요.