OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
vix_roll_yield
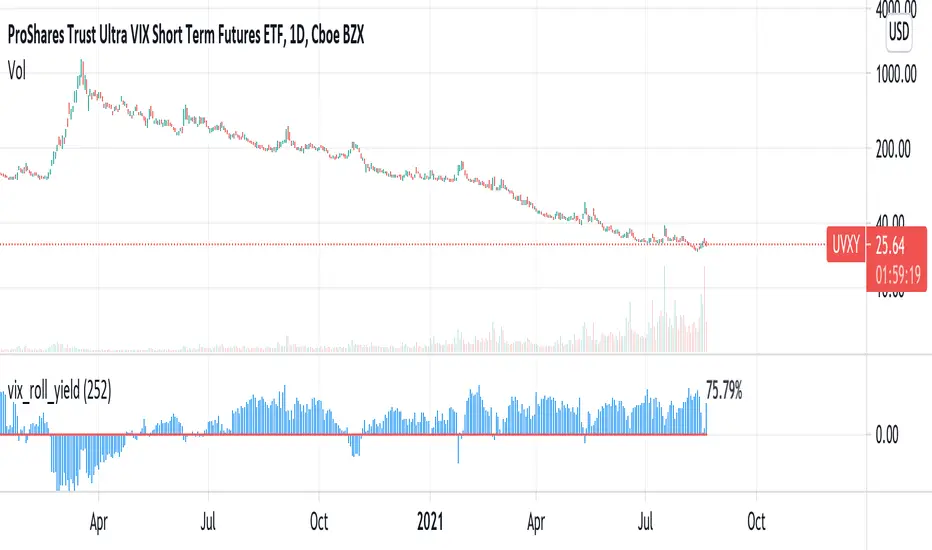
Shows the roll yield of the VX futures, which is the ratio of a continuously weighted average of the front two months to the VIX. The VX (VIX futures) contract expires on the third Tuesday of each month. On the next trading day, the front month will have full weighting, and the second month will have no weight. On the expiration day, the back month will have full weighting and the front month will have no weight. In between, the weight gradually shifts.
This weighted average is similar to the SPVIXSTR index that UVXY and several other funds track. When the average is below the VIX, the indicator is negative, and the front month contract will tend to gain value relatively more rapidly than the back month as it converges upward to the VIX spot price. Because funds whose NAV is tied up in VX contracts continuously roll from the (typically cheaper) front month to the back, in situations where the front month is more expensive than usual--or even more expensive than the back month--these products may have a "tailwind". In this case, they are selling expensive front month contracts to purchase cheap back month contracts.
Ordinarily, VIX funds have a "headwind." The roll yield is positive, the front month is cheap, and the back month is expensive. Day by day the funds sell cheap front month contracts and buy expensive back month contracts, which, in turn and over time, become the front month and converge with the VIX, losing value rapidly. This is a brief explanation about the decay of these products.
This weighted average is similar to the SPVIXSTR index that UVXY and several other funds track. When the average is below the VIX, the indicator is negative, and the front month contract will tend to gain value relatively more rapidly than the back month as it converges upward to the VIX spot price. Because funds whose NAV is tied up in VX contracts continuously roll from the (typically cheaper) front month to the back, in situations where the front month is more expensive than usual--or even more expensive than the back month--these products may have a "tailwind". In this case, they are selling expensive front month contracts to purchase cheap back month contracts.
Ordinarily, VIX funds have a "headwind." The roll yield is positive, the front month is cheap, and the back month is expensive. Day by day the funds sell cheap front month contracts and buy expensive back month contracts, which, in turn and over time, become the front month and converge with the VIX, losing value rapidly. This is a brief explanation about the decay of these products.
오픈 소스 스크립트
트레이딩뷰의 진정한 정신에 따라, 이 스크립트의 작성자는 이를 오픈소스로 공개하여 트레이더들이 기능을 검토하고 검증할 수 있도록 했습니다. 작성자에게 찬사를 보냅니다! 이 코드는 무료로 사용할 수 있지만, 코드를 재게시하는 경우 하우스 룰이 적용된다는 점을 기억하세요.
면책사항
해당 정보와 게시물은 금융, 투자, 트레이딩 또는 기타 유형의 조언이나 권장 사항으로 간주되지 않으며, 트레이딩뷰에서 제공하거나 보증하는 것이 아닙니다. 자세한 내용은 이용 약관을 참조하세요.
오픈 소스 스크립트
트레이딩뷰의 진정한 정신에 따라, 이 스크립트의 작성자는 이를 오픈소스로 공개하여 트레이더들이 기능을 검토하고 검증할 수 있도록 했습니다. 작성자에게 찬사를 보냅니다! 이 코드는 무료로 사용할 수 있지만, 코드를 재게시하는 경우 하우스 룰이 적용된다는 점을 기억하세요.
면책사항
해당 정보와 게시물은 금융, 투자, 트레이딩 또는 기타 유형의 조언이나 권장 사항으로 간주되지 않으며, 트레이딩뷰에서 제공하거나 보증하는 것이 아닙니다. 자세한 내용은 이용 약관을 참조하세요.